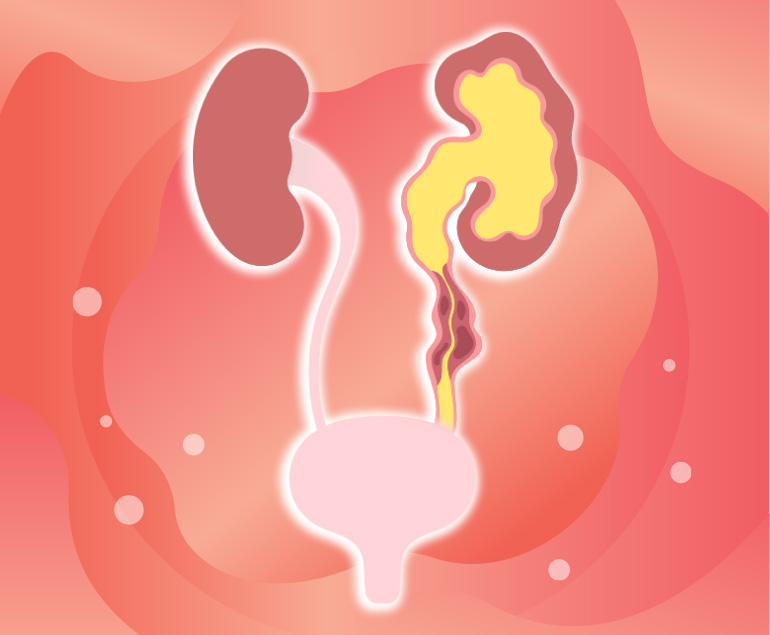
Ureters
The ureter is the duct that runs between the kidney and the bladder. The organ, which is distinguished by its tubular shape, consists of muscle fibers. This organ, which is approximately thirty centimeters long, plays a major role in the excretion of urine from the kidney. The duct that transmits urine to the bladder is located separately from each other in the two kidneys in the body. This organ is like a tunnel and has stenosis in 3 different places. The most notable of these strictures is the entrance to the bladder. The entrance, which has a smaller diameter than the other places where the stenosis appears, is followed by the beginning of the ureter in a place called the linea terminalis.
This organ does not produce stones in itself. The stones seen here are formed when the stone in the kidney falls into the canal. The stone that gets stuck in the stenosis and causes difficulty in urination belongs to the kidney. If the stone is small enough to overcome the stenosis, it can fall naturally.
Ureteral Diseases
Ureteral diseases have features that can disrupt a person’s daily life. In diseases that negatively affect work and social life with the prominent symptoms it shows, it is commonly seen as urinary tract infection (cystitis, inflammation of the urinary tract).
This disease, which can occur due to simple causes such as cold feet, can be prevented by controlling the bacteria in the bladder. Inflammation of the urinary tract, which occurs due to reasons such as incomplete genital hygiene, irregular and unconscious sexual intercourse, exhibits similar characteristics with other disorders seen in the ureters. In this respect, it needs tests in its diagnosis.
Apart from the discomfort diagnosed as a result of urinalysis examination, tumors and stones are also seen in the ureters.
Ureteral Tumor
Ureteral tumor is a very rare tumor. This condition, which we can also call tumors in the bladder, is known as bladder cancer or ureteral cancer among the public and in medicine. This type of cancer, which is much less common than cancer in the kidneys and adrenal glands, exhibits symptoms such as blood in the urine, vomiting, nausea, loss of appetite, weight loss and kidney pain. This disease, which is mostly managed with treatment methods such as open surgery and closed surgery, can be controlled especially with early diagnosis. This condition, which may tend to recur, may occur from scratch due to chronic infections in the ureters, kidney stones, medications used, or may recur even if it is defeated on time.
Ureteral Stone
Ureteral calculi do not form spontaneously in the ureters. This condition, which occurs when the stone formed in the kidney due to various reasons falls into the urinary canal over time, may have a different course of discomfort depending on the size of the stone falling into the canal. For example, the treatment to be followed for medium-sized stones is different than for small-sized stones. Small-sized stones, which can fall with medications used in addition to plenty of water consumption and movement, pass more painlessly than large-sized stones. The condition that heals without surgery requires surgical intervention, especially in large-sized stones. In such cases, the stone is removed after the stone is divided into small pieces (fragmentation).